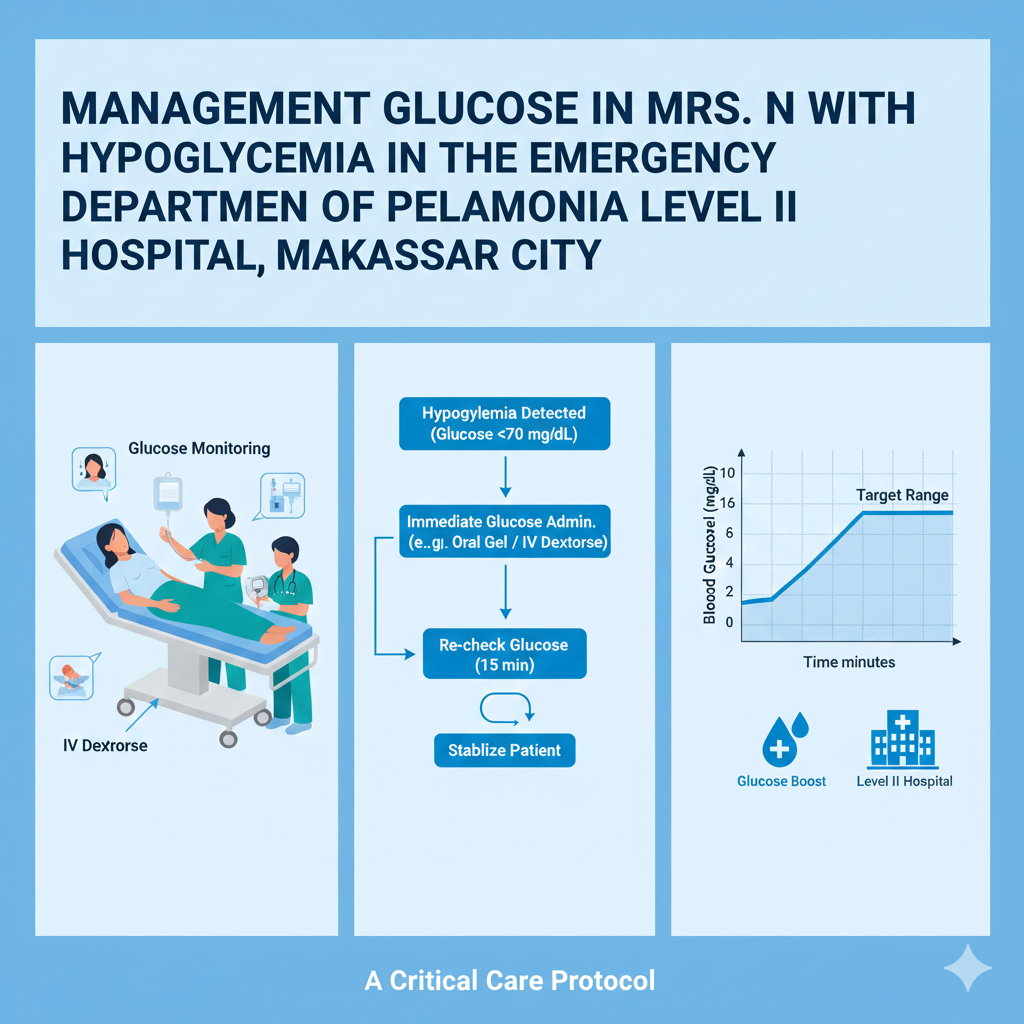
Management Glucose in Mrs. N with Hypoglycemia in the Emergency Department of Pelamonia Level II Hospital, Makassar City
Keywords:
Hypoglycemia, Glucose Management, SugarAbstract
Background: Hypoglycemia is a condition in which blood glucose levels are very low. Hypoglycemia is also common in type 2 diabetes, with a prevalence of 70-80%. Complications of hypoglycemia often occur due to an imbalance between insulin or oral antidiabetic medication administration and food intake, and can be fatal if not treated promptly, given that the brain relies heavily on glucose as its primary energy source. Objective: To analyze the application of hypoglycemia management interventions in one emergency case and to evaluate glucose management in stabilizing the patient's blood glucose levels. Methods: This study used a case study design on Mrs. N (43 years old), who presented to the emergency department with general weakness and a blood glucose level of 60 mg/dl. Nursing interventions focused on hypoglycemia management, specifically collaborative glucose administration, accompanied by glucose management with simple carbohydrates such as sugar water. Administer 15-20 grams of oral carbohydrate or 3-4 tablespoons of granulated sugar dissolved in 250 cc of water, then encourage the patient to sit up and give the patient a drink. Administer sugar water 15-30 minutes later, then re-monitor glucose levels. The evaluation results of the nursing diagnosis of unstable blood glucose levels related to hypoglycemia by checking the GDS after 15 minutes of glucose administration showed improvement at 80 mg/dL. Then at 5:00 PM, the blood glucose level was found to have increased to 113 mg/dL. Then at 8:00 PM, the results improved further to 123 mg/dL.Results: The results of glucose management in the first 15 minutes with the patient's GDS value increased from 60 mg/dL to 80 mg/dL, then in the next 30 minutes it increased to 113 mg/dL, and reached 123 mg/dL.
Conclusion: Hypoglycemia management interventions using sugar water have been shown to be effective in improving blood glucose levels and reducing the risk of complications. This method is recommended as an evidence-based nursing practice for managing emergencies while minimizing mortality from hypoglycemia